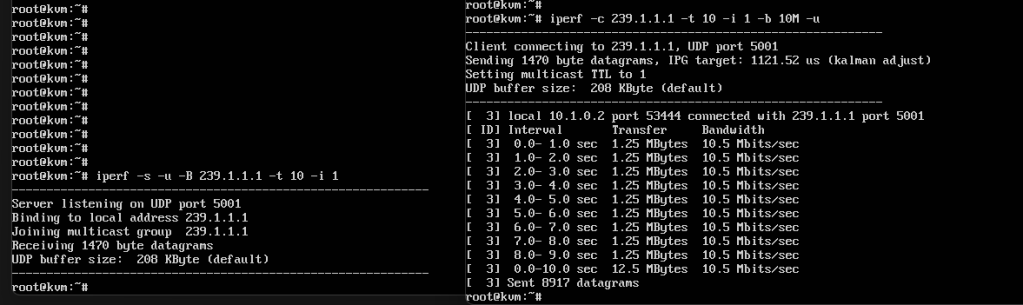
I am using two LINUX machines as source and destination of multicast traffic, using tool called IPERF.
IPERF can be installed and can be used as proxy traffic generator, in our case we are generating multicast traffic on multicast group 239.1.1.1
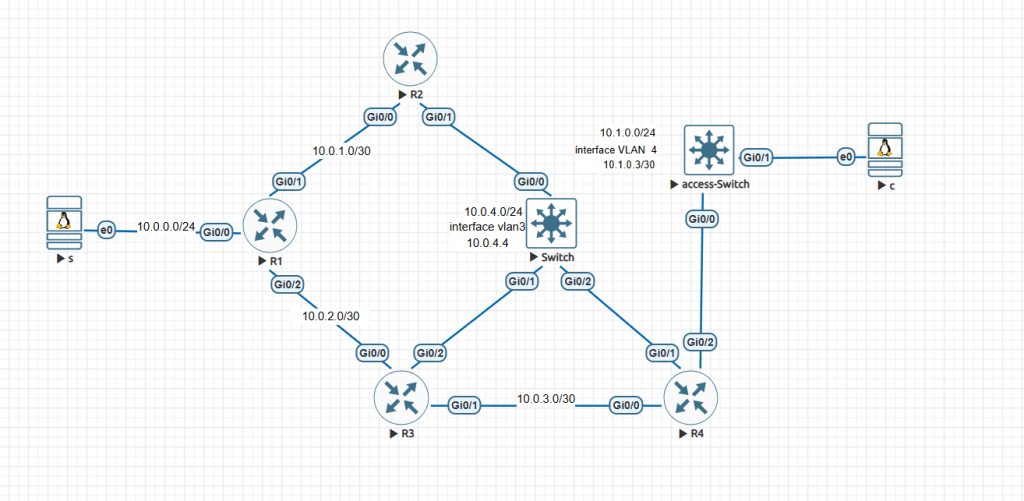
The topology and connectivity diagram that is used is shown below:
Multicast is a protocol that transmits the packets from source to destination hosts only on the hosts that choose to join the multicast group that is allocated to stream or distribute the specific data. PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) and IGMP (Internet Grouper Management Protocol) are the two protocols that work together to make the multicast work. PIM makes the reachability of multicast from source to destination while IGMP manages the joining and maintenance and termination of the membership of clients that join and opt-out from the multicast group.
Enabling PIM sparse mode, and interface configs cab be done with below commands, also we have used OSPF as underlay routing protocol.
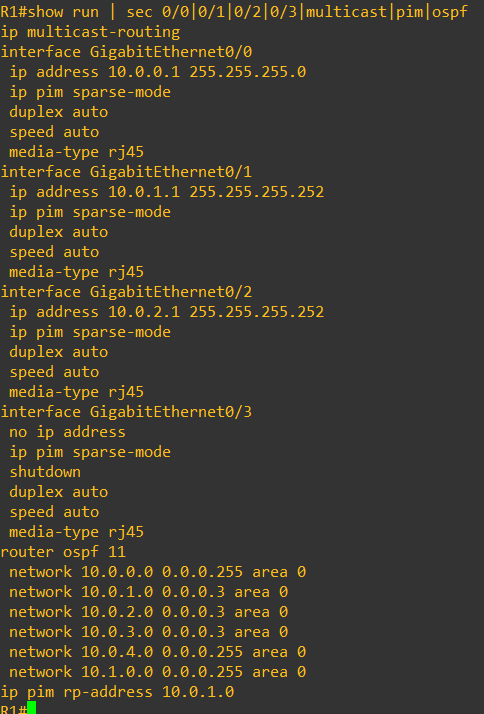
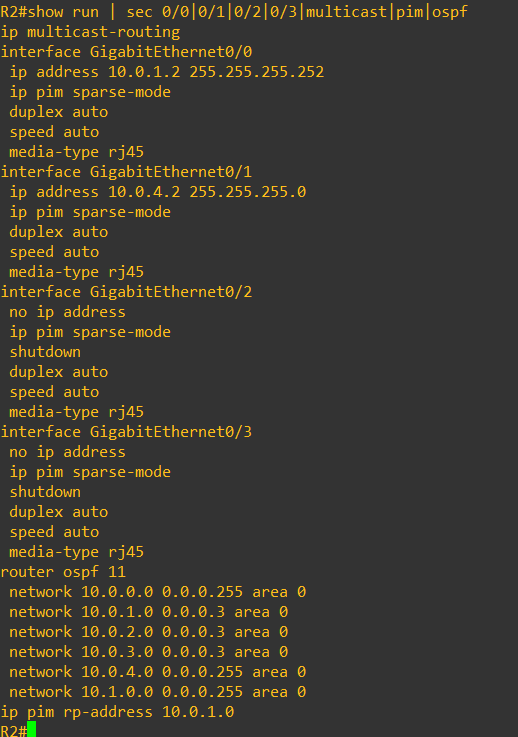
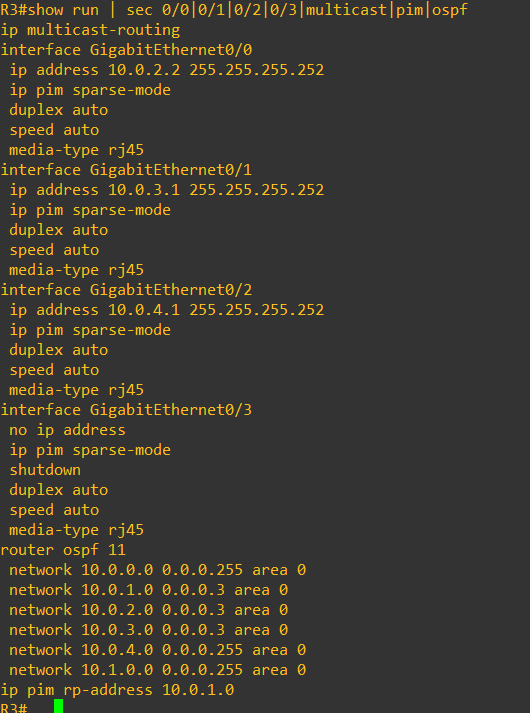
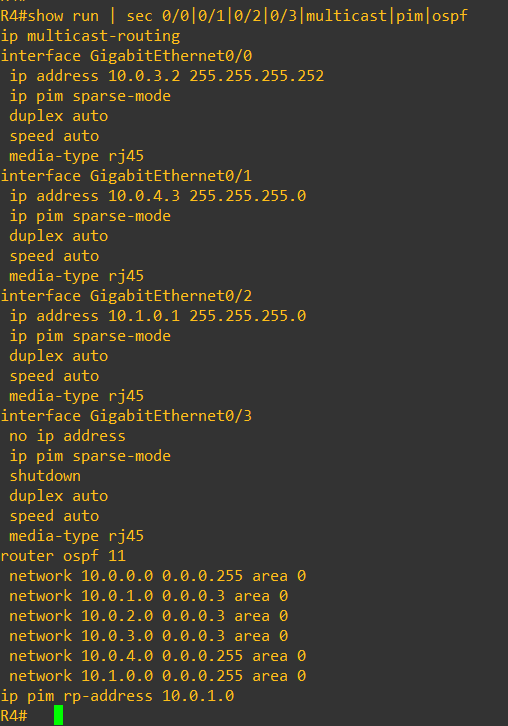
On switches IGMP is by default enabled, while the rest of the configs on switches is pretty simple, only SVI, VLAN and PIM
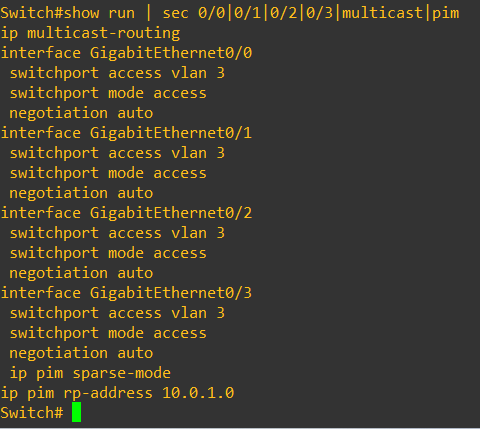
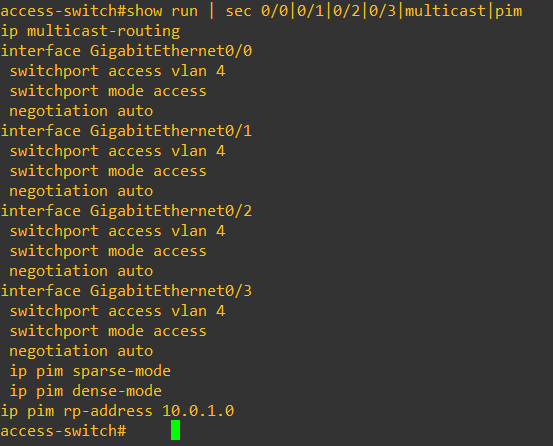
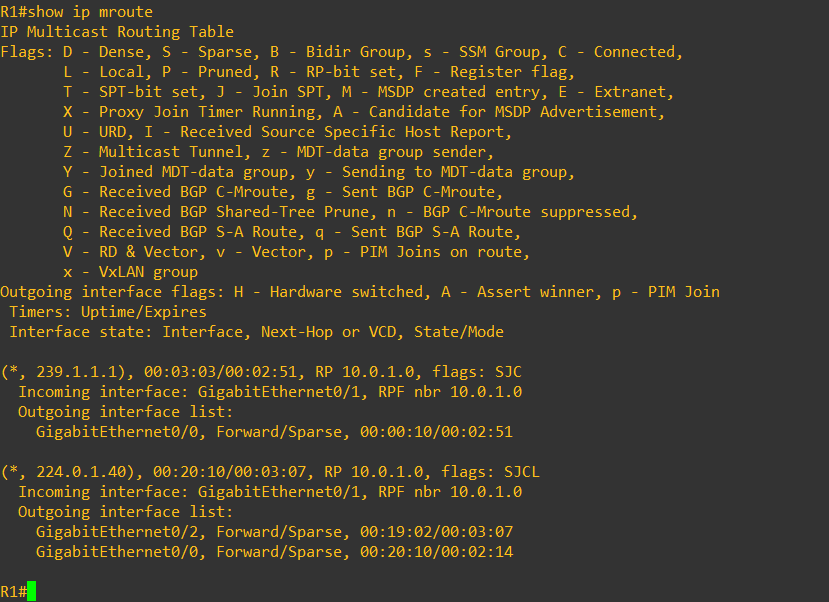
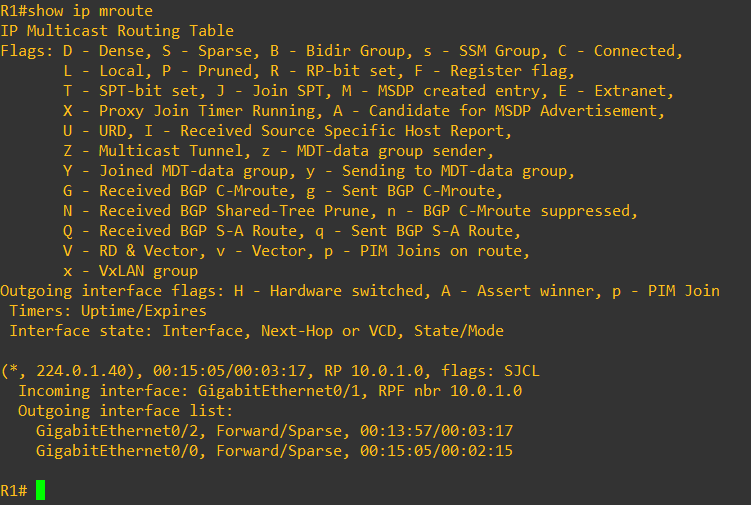
before we start multicast stream, the multicast group is not seen on router’s multicast routing table
As soon as we start the IPERF multicast server, that emulates multicast traffic using respective commands as mentioned in snapshot, one of the LINUX machine acts as source while other as client.
While multicast stream is exchanged, the router shows multicast group in the multicast routing table, as depicted below